Delete Roaming Profile Cache
Having a roaming profile save time for users who hot-desk. However, a roaming profile can cause confusion and slow logon when misused. The killer reason to delete roaming profiles is where you have a ‘Kiosk’ machine with mainly one-off users. What can happen is that the disk fills up with roaming profiles that will never be used again.
Other scenarios where deleting roaming profiles helps are, if you get calls to the helpdesk about broken shortcuts, or error messages saying: ‘Roaming profile cannot be found.’
Topics for Deleting Roaming Profile Cache
- Background to Delete Roaming Cache
- Registry Instructions for DeleteRoamingCache
- Key Learning Points
- Registry Screenshot of DeleteRoamingCache
♦
Logic for Delete Roaming Profiles
The key question with tweaking the registry setting to delete roaming profiles is: ‘Where does the cache get deleted? On the server or the Windows 7 computer?’ The answer is on the machine where you set the value, DeleteRoamingCache=1.
Here is a classic case of checking that your logic matches the registry’s; in this instance, a value of 1 means: no roaming caches gets saved. To be doubly clear, 1 means that all roaming profiles get deleted on that computer
On the other hand, changing to DeleteRoamingCache=0, would be a double negative, (don’t delete), therefore you would end up with roaming profiles!
Background to Delete Roaming Cache
This registry dword, DeleteRoamingCache, controls whether or not, the local computer saves a copy of a user’s roaming profile when users logoff.
Roaming profiles are stored on a server. However, by default, when a user with a roaming profile logsoff, the system saves an additional copy of their profile on the local hard drive. This scheme was designed to give roaming users faster logon, especially when network traffic was busy.
The incentive to change the default behaviour occurs when lots of roaming users logon to one ‘kiosk’ machine. As a result, the disk fills up with profiles, and if it’s unlikely they will ever logon again, you may as well make a registry tweak which deletes these unwanted roaming profiles.
Registry Instructions for DeleteRoamingCache
- Launch Regedit. (See more details on starting regedit)
- Navigate to this path:
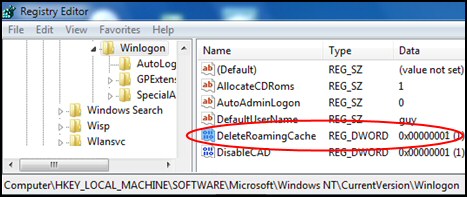
**HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon - Create a new DWORD called DeleteRoamingCache
- Setting a hex value of 00000001 deletes all local roaming profiles.
- See Screenshot below.
Registry Screenshot of DeleteRoamingCache
Guy Recommends: A Free Trial of the Network Performance Monitor (NPM) v11.5
v11.5
SolarWinds’ Orion performance monitor will help you discover what’s happening on your network. This utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; the dashboard will indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or resource overload.
What I like best is the way NPM suggests solutions to network problems. Its also has the ability to monitor the health of individual VMware virtual machines. If you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you try NPM now.
Download a free trial of Solarwinds’ Network Performance Monitor
Update on Delete Roaming Profile Cache
This DeleteRoamingCache registry tweak works in Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000. However, it does not seem delete the roaming profile cache in XP, Vista or Windows 7.
My advice is to abandon the registry and check your Group Policies, look for:
Delete cached copies of roaming profiles
Old Setting for DeleteRoamingCache
Here is an alternative location for DeleteRoamingCache
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\System
While it worked in Windows 2000, again creating a delete roaming profile value in the registry seems to have no effect in XP, Vista or Windows 7.

Key Learning Points
- Check your logic. Especially with the double-negative behavior of: DeleteRoamingCache = 0
- Do you find the DeleteRoamingCache value in HKCU** or HKLM?
Answer: HKLM. - Should you create a value, or modify an existing setting?
Answer: Create a DWORD called: DeleteRoamingCache.
Then assign it a hex value of 00000001 - Is DeleteRoamingCache a String Value or a DWORD?
Answer: DWORD. - Do you need to Restart, or merely Log Off / On?
Answer: Restart the local machine. - Tip: Add this Value, DeleteRoamingCache to Regedit’s Favorites menu.
** HKLM is an abbreviation of HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, and HKCU is shorthand for HKEY_CURRENT_USER. These acronyms are so well-known that you can even use them in .reg files; Vista will understand and obey the registry instruction.
Creating a .Reg File
This page explains how to create, and then edit .reg files for your computer. As it’s easy to import the contents of a .reg file into the registry, do take extra care with procedures. Example DeleteRoamingCache .reg file.
Summary of How to Delete a Roaming Profile Cache on a Windows 7 Computer
This registry tweak had its hey day in Windows 2000. While you can still add DeleteRoamingCache to the registry in Windows 7 it does not seem to have the desired effect of deleting roaming profiles.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
More Windows 7 Registry Tweaks
- Gpedit – Local Group Policy Editor
- Editing the Windows 7 Registry with PowerShell
- PaintDesktopVersion (Build Number)
- Change the Name of a Windows 7 Computer
with LocalizedString - Hide User From Welcome Screen
- RegisteredOwner – Windows 7 Registry Hack
- NoDriveTypeAutoRun
- Delete Roaming Profile Cache
- Windows 7 .Reg Files Examples
- Performance Monitoring