Windows 8 Administrative Shares: ‘Access is Denied’
For security reasons the built-in admin$ family of hidden shares has been disabled in Windows 8.
Windows 8 Administrative Shares
♦
Windows 8 Administrative Shares Access Denied
The situation: you try to connect to a network machine via a hidden share such as c$ or admin$ (\\ MachineName \ c$), and receive an error messages:
- Access is denied.
- The specified username is invalid.
- You may not have permission to use this network share.
Solutions for Access is Denied to Administrative Shares
- One solution may be to accept the situation and abandon your attempt to connect via C$. You could try remote desktop instead. I say this not because the challenge is too difficult, but because the default is the securest configuration for remote user account control (UAC). Once you enable these hidden admin$ shares then your machine can be attacked by hackers. Indeed, that is why Microsoft removed this capability, even though it was popular with XP and Windows 98 users.
- If you really must find a solution to the Windows 8 ‘Access is denied’ message then try leaving the Homegroup.
- If that does not work then Launch Regedit and adjust Remote User Account Control (UAC) settings.
Use Regedit to Create LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy Value
Type Regedit in the Search dialog box, best right-click the executable and ‘Run as administrator’.
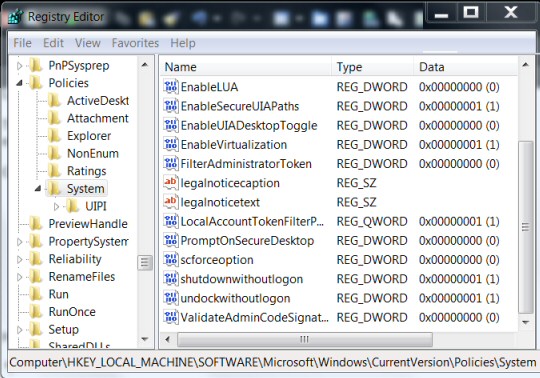
Once Regedit launches navigate to this path:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows
CurrentVersion\Policies\System (See screenshot below)
Once you are at this folder in the registry:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
Recommended: Solarwinds’ Permissions Analyzer – Free Active Directory Tool
I like thePermissions Analyzer because it enables me to see WHO has permissions to do WHAT at a glance. When you launch this tool it analyzes a users effective NTFS permissions for a specific file or folder, and takes into account network share access, then displays the results in a nifty desktop dashboard!
Think of all the frustration that this free SolarWinds utility saves when you are troubleshooting authorization problems for user’s access to a resource. Give this permissions monitor a try – it’s free!
Download SolarWinds’ Free Permissions Analyser – Active Directory Tool
LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy Value Notes
The text book says create a new DWORD value called LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy
What I did was create a QWORD (64-bit) called LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy, that worked for me when the DWORD would not allow access to my 64-bit machine.
In either case, set the value to numeric 1 (meaning on), remember to click OK.
Mostly, the LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy value gets created before you have a chance to set the data value; no problem, just double-click and modify the data from 0 to 1.
Firewall: While I made the connection with the firewall ON. If you cannot get this LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy registry hack to work try adding File and Printer Sharing to the firewall’s Allowed Programs.
The Default Remote Security Situation in Windows 8 and Windows 7
Even if a user is a member of the local administrators group on the remote target, by default, they cannot connect as a full administrator. The user has no elevation potential on the remote computer; thus if the user wants to administer the workstation with a Security Account Manager (SAM) account, it’s best to logon using Remote Desktop. However, as discussed above, you could try creating LocalAccountTokenFilterPolicy.
Guy Recommends: A Free Trial of the Network Performance Monitor (NPM) v11.5
v11.5
SolarWinds’ Orion performance monitor will help you discover what’s happening on your network. This utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; the dashboard will indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or resource overload.
What I like best is the way NPM suggests solutions to network problems. Its also has the ability to monitor the health of individual VMware virtual machines. If you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you try NPM now.
Download a free trial of Solarwinds’ Network Performance Monitor
What Are Admin$ Shares?
Microsoft client operating systems from Windows 95 to XP came with built-in hidden shares such as C$, ADMIN$ and IPC$. Actually, such hidden shares are more commonly used on servers, and are still present on Windows Server 2008 R2.
The purpose of these hidden shares is for administrators, or those in the know, to connect to another machine. Take the scenario where a user at MachineA knows the administrator’s password on MachineB, they could view the files on the other computer by calling for the ‘Run’, or ‘Search’ dialog box and typing:
\\ machineb\c$
At this point they would probably get a request for username and password.
The $ dollar sign means that these network shares never show in the Explorer, indeed I know of administrators who created extra hidden shares simply by appended a regular share with a dollar sign, for example a folder called ‘Stuff’ shared with Stuff$, or even a folder called Stuff shared as Secret$ if you wanted a modicum of security.
Admin$
This hidden share corresponded to the Windows folder, or to be precise, the %Systemroot% folder, thus normally Admin$ would be a hidden share on the C:\Windows folder.
IPC$
The interprocess connect share is used by processes that need to communicate with a client using named pipes, for example domain controllers processing group policies; hence at least some $ shares are still present on the latest Windows servers.
DriveLetter$
As each drive letter is born on a server, (or XP) so the operating system creates the corresponding hidden share, for example D$, E$ and F$. It’s often handy to connect to the root of a drive when you’re not sure of the precise whereabouts of a file you need from a remote machine.
Guy Recommends: SolarWinds’ Log & Event Management Tool
LEM will alert you to problems such as when a key application on a particular server is unavailable. It can also detect when services have stopped, or if there is a network latency problem. Perhaps this log and event management tool’s most interesting ability is to take corrective action, for example by restarting services, or isolating the source of a maleware attack.
Yet perhaps the killer reason why people use LEM is for its compliance capability, with a little help from you, it will ensure that your organization complies with industry standards such as CISP or FERPA. LEM is a really smart application that can make correlations between data in different logs, then use its built-in logic to take corrective action, to restart services, or thwart potential security breaches – give LEM a whirl.
Download your FREE trial of SolarWinds Log & Event Management tool.
The Downfall of Hidden$ Administrative Shares in Windows 8
In a nutshell, hackers and robot computer attacks exploited these hidden shares, forcing Microsoft to take the ruthless approach and disable Windows 8 Administrative shares by default. Actually, this about-turn for built-in share accessibility started with Vista and continued with Windows 7, but at first few people seemed to notice.
Summary of Windows 8 Admin Shares
For security reasons shares such as Admin$ or C$ are no longer created by default on Windows 8 client machines. While there are work-arounds they are fiddly, thus a better solution may be Remote Desktop Connection.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
Microsoft Windows 8 Topics
• Windows 8 Overview • Windows 8 Event Viewer • Win 8 Security Event Log • Log Event Manager
• Win 8 Task Manager • Close Windows 8 Apps • Windows 8 SkipRearm • Windows 8 File History
• Windows 8 App Store • Windows 8 Safely Remove Hardware • Windows 8 Shutdown Command