Active Directory Properties – LDAP* Fields
Here are the common LDAP attributes which correspond to Active Directory properties. They are useful for VBScripts which rely on these LDAP attributes to create or modify objects in Active Directory. For instance if you bulk import users into Active Directory you need to include the LDAP attributes: dn and sAMAccountName.
* LDAP is the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol.
Topics for Active Directory Properties
- Vital LDAP Field
- LDAP Fields from Active Directory Users and Computers
- LDAP Properties for CSVDE and VBScript
- LDAP Examples – Comprehensive List
- Active Directory Permissions Analyzer
♦
Vital LDAP Field – DN Distinguished Name
The keyword ‘distinguished’ means that this attribute is important, and it uniquely defines an Active Directory object. Therefore, each DN must have a unique name and location from all other objects in Active Directory.
Time spent in getting to know the DN attribute will repay many fold. Observe the different components CN=common name, OU = organizational unit. DC often comes with two entries, DC=CP, DC=COM. Note that DC=CP.COM would be wrong. Incidentally in this situation, DC means domain content rather than domain controller.
Another point with the syntax is to check the speech marks; when used with VBScript commands, DN is often enclosed in "speech marks". Even the speech marks have to be of the right type, "double quotes are correct", ‘single quotes may be ignored’ with unpredictable results. Finally, pay particular attention to commas in distinguished names.
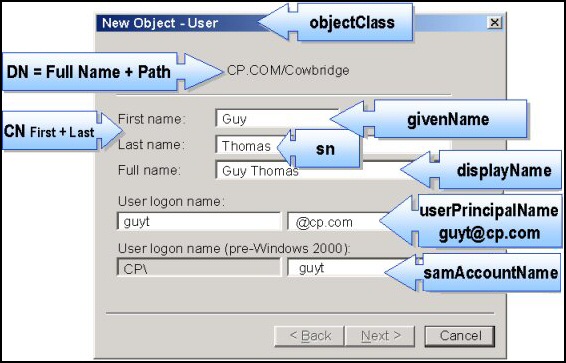
LDAP Fields from Active Directory Users and Computers
The diagram below is taken from Active Directory Users and Computers. It shows the commonest LDAP attributes used in VBScript.
It’s worth spending the time to check how the LDAP attributes map to the Active Directory boxes.
One technique that I like to employ is to add values in the boxes, then export using CSVDE, finally open the file in Excel and search for the value.
LDAP Attribute | Example |
| CN – Common Name | CN=Alan Thomas. Actually, this LDAP attribute is made up from givenName joined to SN. |
| description | What you see in Active Directory Users and Computers. Not to be confused with displayName on the Users property sheet. |
| displayName | displayName = Alan Thomas. Ensure that you understand which field you are configuring. DisplayName can be confused with CN or description. |
| DN – also distinguishedName | DN is simply the most important LDAP attribute. CN=Jimmy Ward, OU= Newport,DC=cp,DC=com |
| givenName | Firstname also called Christian name |
| homeDrive | Home Folder : connect. Tricky to configure |
| name | name = Alan Thomas. Exactly the same as CN. |
| objectCategory | Defines the Active Directory Schema category. For example, objectCategory = Person |
| objectClass | objectClass = User. Also used for Computer, organizationalUnit, even container. Important top level container. |
| physicalDeliveryOfficeName | Office! on the user’s General property sheet |
| profilePath | Roaming profile path: connect. Trick to set up |
| sAMAccountName | sAMAccountName = guyt. Old NT 4.0 logon name, must be unique in the domain. Can be confused with CN. |
| SN | SN = Thomas. This would be referred to as last name or surname. |
| userAccountControl | Used to disable an account. A value of 514 disables the account, while 512 makes the account ready for logon. |
| userPrincipalName | userPrincipalName = [email protected] Often abbreviated to UPN, and looks like an email address. Very useful for logging on especially in a large Forest. Note UPN must be unique in the forest. |
 LDAP NotesDisplay name and Description are different Office’s LDAP attribute is: physicalDeliveryOfficeName E-mail is plain: mail | |
Recommended: Solarwinds’ Permissions Analyzer – Free Active Directory Tool | |
Other LDAP attributesExamples of Exchange Specific LDAP attributes | |
| homeMDB | Here is where you set the MailStore |
| legacyExchangeDN | Legacy distinguished name for creating Contacts. In the following example, Alan Thomas is a Contact in the first administrative group of GUYDOMAIN: /o=GUYDOMAIN/ou=first administrative group/cn=Recipients/cn=Alan Thomas |
| An easy, but important attribute. A simple SMTP address is all that is required [email protected] | |
| mAPIRecipient – FALSE | Indicates that a contact is not a domain user. |
| mailNickname | Normally this is the same value as the sAMAccountName, but could be different if you wished. Needed for mail enabled contacts. |
| mDBUseDefaults | Another straightforward field, just the value to:True |
| msExchHomeServerName | Exchange needs to know which server to deliver the mail. Example: /o=YourOrg/ou=First Administrative Group/cn=Configuration/cn=Servers/cn=MailSrv |
| proxyAddresses | As the name ‘proxy’ suggests, it is possible for one recipient to have more than one email address. Note the plural spelling of proxyAddresses. |
| targetAddress | SMTP:@ e-mail address. Note that SMTP is case sensitive. All capitals means the default address. |
| showInAddressBook | Displays the contact in the Global Address List. |
Other LDAP attributes | |
| c | Country or Region |
| company | Company or organization name |
| department | Useful category to fill in and use for filtering |
| homephone | Home Phone number, (Lots more phone LDAPs) |
| l (Lower case L) | L = Location. City ( Maybe Office |
| location | Important, particularly for printers. |
| manager | Boss, manager |
| mobile | Mobile Phone number |
| ObjectClass | Usually, User, or Computer |
| OU | Organizational unit. See also DN |
| postalCode | Zip or post code |
| st | State, Province or County |
| streetAddress | First line of address |
| telephoneNumber | Office Phone |
Examples of obscure LDAP attributes | |
| dNSHostname | |
| rID | |
| url | |
| uSNCreated, uSNChanged | |
Guy Recommends: SolarWinds’ Free Bulk Import Tool | |
CSVDE -f Exportfile.csv. Then open Exportfile.csv with Excel.exe. Alternatively, use ADSI Edit and right-click the container objects. | |
If you like this page then please share it with your friends