Introduction to Auditing in Windows Server 2003
If you are serious about security, then you must schedule time to examine your security logs. If this means that you are swamped with data, then either filter the events, or change your policy to collect less data. This section concentrates on configuring and interpreting account logon entries in the event viewer.
Topics for Auditing
- Where do you find the audit settings?
- Audit Traps
- Logon Events to look out for
- Failure Code for Event 675
- Failure Code for Event 680
‡
Where do you find the audit settings?
You can configure Windows Server 2003 audit settings in several places. Please check BOTH these locations:
- Active Directory Users and Computers \domain\properties\group policy.
- All Programs, Administrative Tools, Domain Controller Security Policy.
Once you open the policy, navigate to this path: (See Diagram Below)
Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Security Settings\Local Policies\Audit Policy.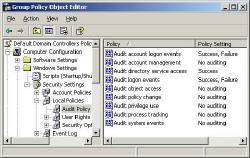
If all else fails then call for the built in help and it will give you a link to the correct path.
Audit Traps
1) Check which policy you are configuring:
Policy for Domain Controllers or the Default Domain Policy
2) Distinguish between these two settings:
- Audit Account Logon – Means people connecting across the network
- Audit Logon Events – Means a keyboard logon, someone at the very Domain Controller
3) The default auditing is for success only, so check the Failure box if you want to see Events 675 and 680.
Logon Events to look out for:
Now we switch to the Event Viewer (All Programs, Administrative Tools). Amongst the numerous events in the Security Log, here are ID numbers to look out for. To refine your search, select View (menu), Filter.
672 An authentication service (AS) ticket was successfully issued and validated.
673 A ticket granting service (TGS) ticket was granted.
674 A security principal renewed an AS ticket or TGS ticket.
675 Pre-authentication failed. This event is generated on a Key Distribution Center (KDC) when a user types in an incorrect password.
678 An account was successfully mapped to a domain account.
680 Successful or Failed logon attempt – see Description
682 A user has reconnected to a disconnected terminal server session.
683 A user disconnected a terminal server session without logging off.
The following events are not generated in Windows XP or in the Windows Server 2003 family. So must come from NT 4.0 or Windows 9x machines.
677 A TGS ticket was not granted.
676 Authentication ticket request failed.
681 Logon failure. A domain account logon was attempted.
Guy Recommends: SolarWinds’ Log & Event Management Tool
LEM will alert you to problems such as when a key application on a particular server is unavailable. It can also detect when services have stopped, or if there is a network latency problem. Perhaps this log and event management tool’s most interesting ability is to take corrective action, for example by restarting services, or isolating the source of a maleware attack.
Yet perhaps the killer reason why people use LEM is for its compliance capability, with a little help from you, it will ensure that your organization complies with industry standards such as CISP or FERPA. LEM is a really smart application that can make correlations between data in different logs, then use its built-in logic to take corrective action, to restart services, or thwart potential security breaches – give LEM a whirl.
Download your FREE trial of SolarWinds Log & Event Management tool.
Failure Codes for Event 675 – see diagram.
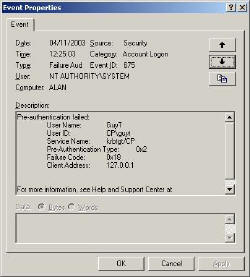 Use the View (Menu) filter and enter 675 in the Event ID. If you do not get any of these events, then deliberately logon to the domain controller with the wrong password or account.
Use the View (Menu) filter and enter 675 in the Event ID. If you do not get any of these events, then deliberately logon to the domain controller with the wrong password or account.
Once you double click an event check the extra information in the Description.
Here are some useful codes:
0x6 The username does not exist
0x17 The account has expired
0x18 Username exists, but password is wrong
0x25 Workstation’s clock is out of synch
Troubleshooting: if you do not get any 675 when you log on with the wrong password check Traps.
Failure codes that you see with event ID 680
3221225572 User logon with misspelled user account
3221225578 User logon with misspelled password
3221225584 User logon from unauthorized workstation
3221225585 User logon with expired password
3221225586 User logon to account disabled
3221225875 User logon with expired account
3221226036 User logon with account locked
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
Related topics
• Accounts • Auditing • IPSec • Kerberos Tickets • Windows RIS Server