Administrative Privileges in Vista
The most frustrating problem with Vista is when you are logged on as an administrator, yet you still don’t have the rights or permissions to configure a setting. Fortunately, there are two solutions. Firstly, I will show you how to find the, ‘Run as administrator’ option. Secondly, I will explain how to activate THE Administrator’s account.
Topics for Vista Administrative Privileges
- How to ‘Run as administrator’
- Programs that need elevated privileges
- Position of The Administrator Accounts
- Position of UAC (User Accounts Manager)
- Related Problem – Administrative Permissions
- Summary of Administrative Privileges
♦
How to ‘Run as administrator’
For security reasons, Vista has been designed so that for normal operations even administrators work with ordinary user ‘tokens’. When an administrator needs elevated rights, they either click ‘Continue’ in the UAC box, or seek the ‘Run as administrator’ option.
The key to this ‘Run as administrator’ technique is to identify the master program. My point is that while Ipconfig may report an error such as, ‘The requested operation requires elevation’, the problem lies with the master program, cmd.exe, and not Ipconfig. Don’t blame the passenger for the sins of the driver.
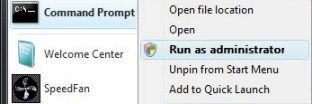
Method 1: Right-click
- Right-click the master program, for example: Command Prompt.
- Select – ‘Run as administrator’ from the shortcut menu.
- See screenshot below.
Method 2: Ctrl +Shift +Enter
Once again find the key executable, but instead of launching it by clicking with the mouse, press this keyboard combination: Ctrl +Shift +Enter. One clue that this method has worked is that the Command Prompt’s title bar says ‘Administrator: Command Prompt’.
Method 3: Shortcut, Advanced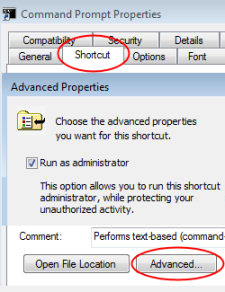
This shortcut method is my favorite. It is a variation of method 1; the idea is to configure ‘Run as administrator’, not just for that one session, but permanently.
- Right-click the Command Prompt executable
- Select Properties from the drop-down menu
- Select the Shortcut (tab)
- Click on Advanced (button)
- Tick: Run as administrator
- See screenshot opposite
Programs that need elevated privileges
- Cmd – (For Ipconfig, NetSh and other command line programs)
- Task Scheduler
- Regedit
- Regsvr32 – Registering DLLs (Note the sequence of the letters svr in Regsvr32)
- There will be more! Whatever the program, seek this ‘Run as administrator’ method.
Guy Recommends: A Free Trial of the Network Performance Monitor(NPM) v11.5
v11.5
SolarWinds’ Orion performance monitor will help you discover what’s happening on your network. This utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; the dashboard will indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or resource overload.
What I like best is the way NPM suggests solutions to network problems. Its also has the ability to monitor the health of individual VMware virtual machines. If you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you try NPM now.
Download a free trial of Solarwinds’ Network Performance Monitor
Position of The Administrator Accounts
Remember that Vista is obsessed with security. For the good of keeping out viruses, even administrator accounts are restricted. The only way to retain your sanity, is to accept that sometimes you have to take the extra step and ‘Run as administrator’.
However, Vista has a hidden-super user account, which is called precisely ‘Administrator’. This is the only account that is exempt from the need to ‘Run as administrator’, all other accounts who are members of the local administrators group, still need elevated rights to perform many command line tasks. See here how you Activate this special Vista Administrator account.
Position of UAC (User Accounts Manager)
Regarding elevated privileges, I can sum up the position of the UAC in two words, ‘forget it’. What I mean is whether you enable or disable the UAC, it has no effect on the need to gain the elevated privileges by invoking ‘Run as administrator’. My advice is go with the flow. Brush aside the indignation that you reversed the UAC and still Ipconfig / renew complained about needing ‘Elevated privileges’.
Related Problem – Administrative Permissions
One problem that administrative accounts face is being denied permission to certain folders. While Vista’s behavior is new, disconcerting and irritating – it is by design. Fortunately, there is a straightforward solution. Either up pops the nagging UAC and you simply say ‘Continue’, and thus gain permission, or you have to select, Properties and the security tab. As an administrator you have the right to add yourself to the Security tab. Once again The Administrator, the super-user account that you have to activate, is exempt from any permission restrictions.
Summary of Administrative Privileges
For the highest privileges, with zero nagging, activate THE Administrator. For other accounts, who gain rights and privileges by being a member of the administrators, they still have to ‘Run as administrator’. Probably the best way to elevate your privileges is to find the shortcut’s Advanced menu, and tick the box.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
Configuring Windows Vista Topics:
| Vista Tools and Extras
|
Download Your Tweak the Registry Ebook for only $6.45 This ebook will explain the workings of the registry. I thoroughly enjoy tweaking the registry, and I want to distill the best of my experiences and pass them on to you. Each registry tweak has two aims; to solve a specific problem, and to provide general learning points, which help you to master regedit. Over 60 pages ebook and PDF format
| |

