Conditional Forwarding in Windows 2003 DNS
If you think carefully about the two words, Conditional and Forwarding then this feature becomes self explanatory. Deeper thought raises more problems than it solves. What condition? Where does it forward? Above all where do find this feature.
Configuring Conditional Forwarding
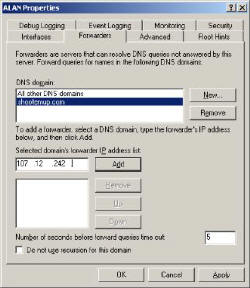
Let us begin by discovering where you configure Conditional Forwarding. Start at the server icon in the DNS snap-in (not the Forward Lookup Zone). right-click, properties, Forwarders (Tab).
Take the scenario where shootemup.com is an associate of your organization. Moreover, your users are for ever querying their server. If shootemup.com kindly provide the IP address of their server which is authoritative for shootemup.com then you can configure that server as a conditional forwarder.
To summarise, the Condition is that one of your clients query is for shootemup.com. The Forwarding is to the IP address specified at the Forwarders tab of your DNS server.
So what would happen without Conditional Forwarding? The answer is that your server would ‘ walk the root hints ‘. The server (Alan in the diagram), contacts the root server ‘ . ‘ on the internet. The root server forwards your request to the .com server who in turn forwards the request to shootemup.com’s server.
In a nutshell, Conditional Forwarding is like taking a short cut.
One last question, what happens if your clients query someonelse.org. The answer is that your server goes the long way around and ‘ walks the root hints ‘. Unless of course you are friendly with someonelse.org and configure another Conditional Forwarder.
Guy Recommends: A Free Trial of the Network Performance Monitor (NPM) v12
v12
SolarWinds’ Network Performance Monitor will help you discover what’s happening on your network. This utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; the dashboard will indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or resource overload.
Perhaps the NPM’s best feature is the way it suggests solutions to network problems. Its second best feature is the ability to monitor the health of individual VMware virtual machines. If you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you give this Network Performance Monitor a try.
Download your free trial of SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor.
Summary
DNS in Windows 2000 was a huge improvement over NT4.0 Windows Server 2003 new DNS features iron out a few problems, add a few new features which speed up performance in large forests.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
Related DNS Server topics
- New Features for DNS in Windows Server 2003
- DNS – Names & Namespace
- Types of DNS Zone
- Conditional Forwarding
- Installing DNS Server
- DNS Queries
- Root Hints
- Resource Records
- DNS Naming Rules
- Basic DNS Server Troubleshooting
- Advanced DNS Troubleshooting
- Debug Logging for DNS in Windows Server 2003
- DNSLint – Utility