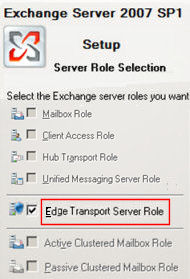
Exchange 2007 – Install the Edge Transport Server Role
In Exchange 2007, the Edge Transport server is in different category from the other roles. It has special requirements because it’s outside of your Active Directory, and it’s also on the external side of your firewall.
The following outline and screenshots were kindly supplied by Alain Laventure.
Topics for Exchange 2007 Edge Server Role
- Requirements for the Exchange 2007 Edge Server Role
- Workgroup
- ADAM or AD LDS
- Install Exchange 2007
- EdgeSync
- Ports Required by the Edge Server
- Hub Server Role
- Subscriptions
- Troubleshooting Edge Server Queues
- Summary – Edge Transport Server Role in Exchange 2007
♠
Requirements for the Exchange 2007 Edge Server Role
If you keep in mind that the purpose of the Edge role is security, then the reasons behind these particular and precise requirements, become clearer.
Planning
Remember that you need 64-bit hardware when you install the underlying operating system on, either Windows Server 2008, or Windows Server 2003.
As for the placement of your Edge Transport Server, it should be in the perimeter network, and certainly outside the main network firewall.
Workgroup – You should prepare a stand-alone server for the Edge Transport Role. The Edge server is exposed to the internet, and because it’s running Exchange 2007 server, it becomes a likely target for hackers and spammers. Thus, if this Edge server in a workgroup then it has no information about your domain, and consequently, your administrative usernames and passwords cannot be compromised.
ADAM (Active Directory Application Mode) – If you have ever wondered what was the point of this alternative active directory, then planning the Edge server will act as a case study for the use of ADAM. Note, in Windows Server 2008 the equivalent of ADAM is AD LDS (Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services).
The point is that although the Edge server is in a workgroup, it still needs a few basic Active Directory capabilities, in particular, it needs to know how to send (forward) appropriate email to your domain recipients.
Install Exchange 2007
- Insert the Exchange 2007 setup disk.
- Install (Add) the Edge Server Role.
- Take the time for a Readiness Check.
EdgeSync – Remember that the Edge Transport server doesn’t have access to your domain’s Active Directory directory service. The role of Microsoft’s EdgeSync is to copy a subset of Active Directory information and ‘paste’ it into the Edge server’s directory service (AD LDS or ADAM). Rest assured, EdgeSync does not send any information back to Active Directory, thus there is no backdoor for hackers to exploit.
During this one-way transfer, only a specialist sub-set of Active Directory gets copied, mainly data about the connection configuration, but also anti-spam information. Without this information the Edge server would not know where to send incoming email, which is addressed to your Exchange 2007 recipients.

Ports Required by the Edge Server
| Port | Protocol | Reason | |
| Internet | 25 Tcp | Smtp | |
| Internal Network | 25 Tcp | Smtp | |
| Internal Network | 50636 Tcp | Secure LDAP | EdgeSync |
Guy Recommends: A Free Trial of the Network Performance Monitor (NPM) v11.5
v11.5
SolarWinds’ Network Performance Monitor will help you discover what’s happening on your network. This utility will also guide you through troubleshooting; the dashboard will indicate whether the root cause is a broken link, faulty equipment or resource overload.
What I like best is the way NPM suggests solutions to network problems. Its also has the ability to monitor the health of individual VMware virtual machines. If you are interested in troubleshooting, and creating network maps, then I recommend that you try NPM now.
Download a free trial of SolarWinds’ Network Performance Monitor
Hub Server Role – The Edge Server communicates with one of the internal Exchange 2007 servers that has the Hub Server Role. Specifically, the Edge Rules agent filters unwanted messages and thus reduces the spam that enters your Exchange organization. To manage the Edge Rules agent, launch the Exchange Management Console. Experiment with different conditions, exceptions, actions, and the scope until you have the desired level of filtering.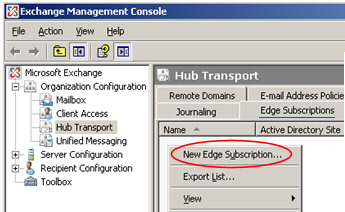
Edge Subscriptions – You can manage the Edge subscription and synchronization processes with the EdgeSubscription family of PowerShell cmdlets. To setup subscriptions follow this export –> import sequence.
On the Edge Server (Export)
New-EdgeSubscription -Filename c:\scripts\EdgeSubscriptionFile.xml
On the Hub Transport Server (Import)
Copy the file EdgeSubscriptionFile.xml from the Edge server.
Open the Exchange Management Console, expand the Organization Configuration and select Hub Transport. Now you are ready to call the New Edge Subscription wizard, browse for the filename (EdgeSubscriptionFile.xml), the wizard will complete the subscription.
Edge Transport DNS – This server sees every message that comes into your organization. You should also configure DNS so that your domain’s external Mail Exchange (MX) record points to the Edge Server. Once all the components are configured, Exchange 2007 automatically routes outgoing mail through the Edge Transport Service.
Redundancy There is no reason (other than cost) not to install a second Edge Transport Server; the benefits would be redundancy, and possibly load balancing.
Troubleshooting Edge Server Queues
Problem at the Edge Server
In the Queue Viewer, you see messages displaying the error message:
451 5.7.3 ‘Cannot achieve Exchange Server authentication’.
Solve the Problem in the Exchange Management Console
- Navigate to Server Configuration –> Hub Transport
- Right-click the Receive connector, and then select Properties.
- Select the Authentication tab.
- Check the Transport Layer Security (TLS) check box.
- Check the Exchange Server authentication check box.
- Click Apply.
Synchronize with the Hub Server
To complete the job, force synchronization with one of these PowerShell commands.
Start-EdgeSynchronization [Exchange 2007 RTM]
Start-EdgeSynchronization -server HubServerName [Exchange SP1]
Guy Recommends: SolarWinds Free Wake-On-LAN Utility
Encouraging computers to sleep when they’re not in use is a great idea – until you are away from your desk and need a file on that remote sleeping machine!
WOL also has business uses for example, rousing machines so that they can have update patches applied. My real reason for recommending you download this free tool is because it’s so much fun sending those ‘Magic Packets’. Give WOL a try – it’s free.
Download your free copy of SolarWinds Wake-On-LAN
Troubleshooting DNS Problems
400 4.4.7 Message Delayed
451 4.4.0 DNS Query Failed
Solution – Call for your ‘Toolbox’
Select Mail flow tools category
Open the Queue Viewer
Check that you have an inbound message queue for an accepted domain, such as "MyCompany.com", and if there is an error similar to "451 4.4.0 DNS Query Failed".
Troubleshooting:
- Select the Edge server in the Result pane, and then select Properties.
- Find the Internal DNS Lookups tab.
- Select: All Available.
- If you have multiple NIC adapters, select the one is for the internal network, select ‘Use network card DNS settings’. The IP addresses will magically populate the box with the DNS server IP addresses from the internal network card.
- Don’t reboot, but Restart the Transport service.
If you have only one network card, there are two options:
You can select ‘Use these DNS servers’ and then select the IP address of the internal DNS server. Alternatively, you can add a host file containing the DNS server information.
Guy Recommends: SolarWinds’ Free Bulk Mailbox Import Tool
Import users from a spreadsheet, complete with their mailbox. Just provide a list of the users with the fields in the top row, and save as .csv file. Then launch this FREE utility, match your Exchange fields with AD’s attributes, click and import the users. Optionally, you can provide the name of the OU where the new mailboxes will be born.
There are also two bonus tools in the free download, and all 3 have been approved by Microsoft:
- Bulk-import new users and mailboxes into Active Directory.
- Seek and zap unwanted user accounts.
- Find inactive computers.
Download your FREE bulk mailbox import tool.
Summary – Edge Transport Server Role in Exchange 2007
In a nutshell, the Edge Transport Server is your Exchange 2007 security outpost. Thus, it is best to deploy this server in your organization’s perimeter network. For these security reasons, it makes sense to install the Edge role on a stand-alone server in a Workgroup. This Edge Transport server then communicates with the Hub Server, (which has Active Directory) through the EdgeSync service.
Credit and acknowledgement
Alain Laventure provided the screenshots, the detailed steps and the background for this article on the Edge Transport Server Role.
If you like this page then please share it with your friends
See more Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 topics:
• Exchange 2007 Home • SP1 • Migration Advice • Transition Checklist • Compatibility • Edge
• Install • Server Roles • CAS Role • Hub Transport • SMTP Connector • Exchange CCR • ExBPA
• Mailbox Role • Create Mailbox • Mailbox Stores • Recipients • GAL • Free Syslog Analyser